1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <math.h>
unsigned long long rdtsc(){
asm("rdtsc");
}
char* slow_memcpy(char* dest, const char* src, size_t len){
int i;
for (i=0; i<len; i++) {
dest[i] = src[i];
}
return dest;
}
char* fast_memcpy(char* dest, const char* src, size_t len){
size_t i;
if(len >= 64){
i = len / 64;
len &= (64-1);
while(i-- > 0){
__asm__ __volatile__ (
"movdqa (%0), %%xmm0\n"
"movdqa 16(%0), %%xmm1\n"
"movdqa 32(%0), %%xmm2\n"
"movdqa 48(%0), %%xmm3\n"
"movntps %%xmm0, (%1)\n"
"movntps %%xmm1, 16(%1)\n"
"movntps %%xmm2, 32(%1)\n"
"movntps %%xmm3, 48(%1)\n"
::"r"(src),"r"(dest):"memory");
dest += 64;
src += 64;
}
}
if(len) slow_memcpy(dest, src, len);
return dest;
}
int main(void){
setvbuf(stdout, 0, _IONBF, 0);
setvbuf(stdin, 0, _IOLBF, 0);
printf("Hey, I have a boring assignment for CS class.. :(\n");
printf("The assignment is simple.\n");
printf("-----------------------------------------------------\n");
printf("- What is the best implementation of memcpy? -\n");
printf("- 1. implement your own slow/fast version of memcpy -\n");
printf("- 2. compare them with various size of data -\n");
printf("- 3. conclude your experiment and submit report -\n");
printf("-----------------------------------------------------\n");
printf("This time, just help me out with my experiment and get flag\n");
printf("No fancy hacking, I promise :D\n");
unsigned long long t1, t2;
int e;
char* src;
char* dest;
unsigned int low, high;
unsigned int size;
char* cache1 = mmap(0, 0x4000, 7, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0);
char* cache2 = mmap(0, 0x4000, 7, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0);
src = mmap(0, 0x2000, 7, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0);
size_t sizes[10];
int i=0;
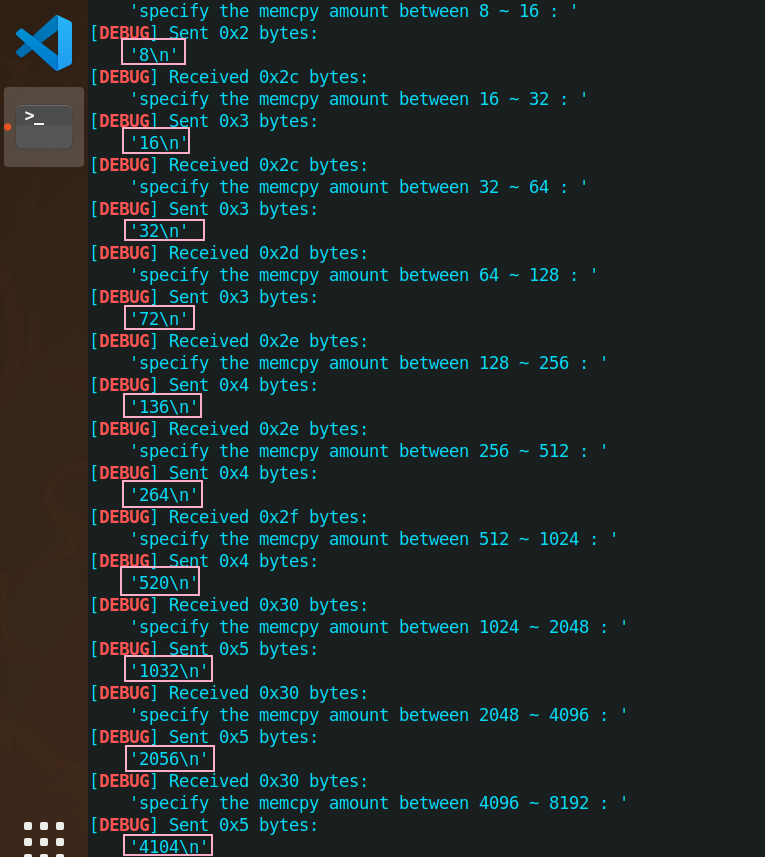
for(e=4; e<14; e++){
low = pow(2,e-1);
high = pow(2,e);
printf("specify the memcpy amount between %d ~ %d : ", low, high);
scanf("%d", &size);
if( size < low || size > high ){
printf("don't mess with the experiment.\n");
exit(0);
}
sizes[i++] = size;
}
sleep(1);
printf("ok, lets run the experiment with your configuration\n");
sleep(1);
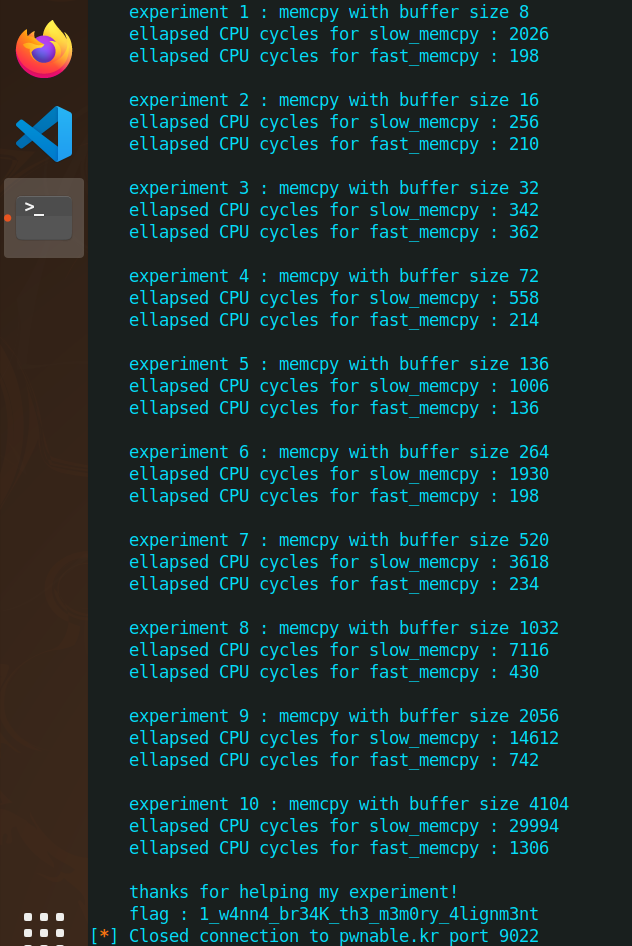
for(i=0; i<10; i++){
size = sizes[i];
printf("experiment %d : memcpy with buffer size %d\n", i+1, size);
dest = malloc( size );
memcpy(cache1, cache2, 0x4000);
t1 = rdtsc();
slow_memcpy(dest, src, size);
t2 = rdtsc();
printf("ellapsed CPU cycles for slow_memcpy : %llu\n", t2-t1);
memcpy(cache1, cache2, 0x4000);
t1 = rdtsc();
fast_memcpy(dest, src, size);
t2 = rdtsc();
printf("ellapsed CPU cycles for fast_memcpy : %llu\n", t2-t1);
printf("\n");
}
printf("thanks for helping my experiment!\n");
printf("flag : ----- erased in this source code -----\n");
return 0;
}
|